Module 3: Introduction to WGBS and Analysis
Important notes:
- Please refer to the following guide for instructions on how to connect to Guillimin and submit jobs: using_the_guillimin_hpc.md
- The instructions in this tutorial will suppose you are in a Linux/Max environment. The equivalent tools in Windows are provided in the Guillimin documentation.
- The user class99 is provided here as an example. You should replace it by the username that was assigned to you at the beginning of the workshop.
Introduction
Description of the lab
This module will cover the basics of Bisulfite-sequencing data analysis including data visualization in IGV.
Local software that we will use
- ssh
- IGV
Tutorial
Getting started
Connect to the Guillimin HPC
ssh class99@guillimin.clumeq.ca
You will be in your home folder. At this step, before continuing, please make sure that you followed the instructions in the section “The first time you log in” of the Guillimin guide. If you don’t, compute jobs will not execute normally.
Prepare directory for module 3
rm -rf ~/module3
mkdir -p ~/module3
cd ~/module3
Copy data for module 3
mkdir data
cp /gs/project/mugqic/bioinformatics.ca/epigenomics/wgb-seq/data/* data/.
Check the files
By typing ls you should see something similar to this
[class99@lg-1r17-n02 module3]$ ls data
iPSC_1.1.fastq iPSC_1.2.fastq iPSC_2.1.fastq iPSC_2.2.fastq
What do the “.1” and “.2” in the file names mean?
Map using bismark
We will now process and map the reads using Bismark.
echo 'module load mugqic/bismark/0.16.1 ; \
bismark --bowtie2 -n 1 /gs/project/mugqic/bioinformatics.ca/epigenomics/wgb-seq/genome/ \
-1 data/iPSC_1.1.fastq -2 data/iPSC_1.2.fastq' \
| qsub -l nodes=1:ppn=4 -d .
The -n 1 defines the maximum number of mismatches permitted in the seed.
The /gs/project/mugqic/bioinformatics.ca/epigenomics/wgb-seq/genome/ specifies the reference genome to use.
The qsub -l nodes=1:ppn=4 -d . submits the job to the cluster using 1 node, 4 processors and the current directory for output.
For more details, please refer to the Bismark user guide.
Check status of your job
watch -d showq -uclass%%
Replace “%%” by your student number.
Check files
[class99@lg-1r17-n02 module3]$ ls
data iPSC_1.1.fastq_C_to_T.fastq iPSC_1.2.fastq_G_to_A.fastq STDIN.e60392282 STDIN.o60392282
Is this what you expected?
Check the error message
less STDIN.e60392282
Where you replace the file name by your specific error file.
Map (again) using bismark
rm iPSC_*
rm STDIN.*
echo 'module load mugqic/bismark/0.16.1 ; module load mugqic/bowtie2/2.2.4 ; module load mugqic/samtools/1.3 ; \
bismark --bowtie2 -n 1 /gs/project/mugqic/bioinformatics.ca/epigenomics/wgb-seq/genome/ \
-1 data/iPSC_1.1.fastq -2 data/iPSC_1.2.fastq' \
| qsub -l nodes=1:ppn=4 -d .
Check the files as the are being written
watch -d ls -ltr
Check files
At the end, you should have something similar to
[class99@lg-1r17-n02 module3]$ ls -ltr
total 13760
drwxr-xr-x 2 class99 class 512 Jun 20 16:56 data
-rw------- 1 class99 class 5107 Jun 20 17:21 STDIN.e60392695
-rw-r--r-- 1 class99 class 13964455 Jun 20 17:21 iPSC_1.1_bismark_bt2_pe.bam
-rw-r--r-- 1 class99 class 1862 Jun 20 17:21 iPSC_1.1_bismark_bt2_PE_report.txt
-rw------- 1 class99 class 4405 Jun 20 17:21 STDIN.o60392695
Let’s look at the report
less iPSC_1.1_bismark_bt2_PE_report.txt
Prepare files for loading in IGV
We need to sort the bam file and prepare an index so we will be able to load in IGV. We will use the program samtools for this.
echo 'module load mugqic/samtools/1.3 ; \
samtools sort iPSC_1.1_bismark_bt2_pe.bam -o iPSC_1.1_bismark_bt2_pe_sorted.bam ; \
samtools index iPSC_1.1_bismark_bt2_pe_sorted.bam' \
| qsub -l nodes=1:ppn=1 -d .
Check files
At the end, you should have something similar to
[class99@lg-1r17-n02 module3]$ ls -ltr
total 27136
drwxr-xr-x 2 class99 class 512 Jun 20 16:56 data
-rw------- 1 class99 class 5107 Jun 20 17:21 STDIN.e60392695
-rw-r--r-- 1 class99 class 13964455 Jun 20 17:21 iPSC_1.1_bismark_bt2_pe.bam
-rw-r--r-- 1 class99 class 1862 Jun 20 17:21 iPSC_1.1_bismark_bt2_PE_report.txt
-rw------- 1 class99 class 4405 Jun 20 17:21 STDIN.o60392695
-rw------- 1 class99 class 61 Jun 20 17:25 STDIN.e60393634
-rw-r--r-- 1 class99 class 11653618 Jun 20 17:25 iPSC_1.1_bismark_bt2_pe_sorted.bam
-rw------- 1 class99 class 846 Jun 20 17:25 STDIN.o60393634
-rw-r--r-- 1 class99 class 1967480 Jun 20 17:25 iPSC_1.1_bismark_bt2_pe_sorted.bam.bai
Copy files to your local computer to view in IGV
Using a different terminal window that is not connected to the server (if you are using Mac/Linux) or WinSCP (if you are using Windows), retrieve the iPSC_1.1_bismark_bt2_pe_sorted.bam and iPSC_1.1_bismark_bt2_pe_sorted.bam.bai
scp class%%@guillimin.clumeq.ca:/home/class%%/module3/iPSC_1.1_bismark_bt2_pe_sorted.bam* .
Where you need to replace the two places with “%%” by your student number.
Load data and explore using IGV
Launch IGV on your computer.
Load your sorted bam and index file in IGV using File -> Load from file.
Go to:
chr3:43,375,889-45,912,052
And zoom in until you see something.
For instance go to:
chr3:44,513,532-44,523,018
You should see something like
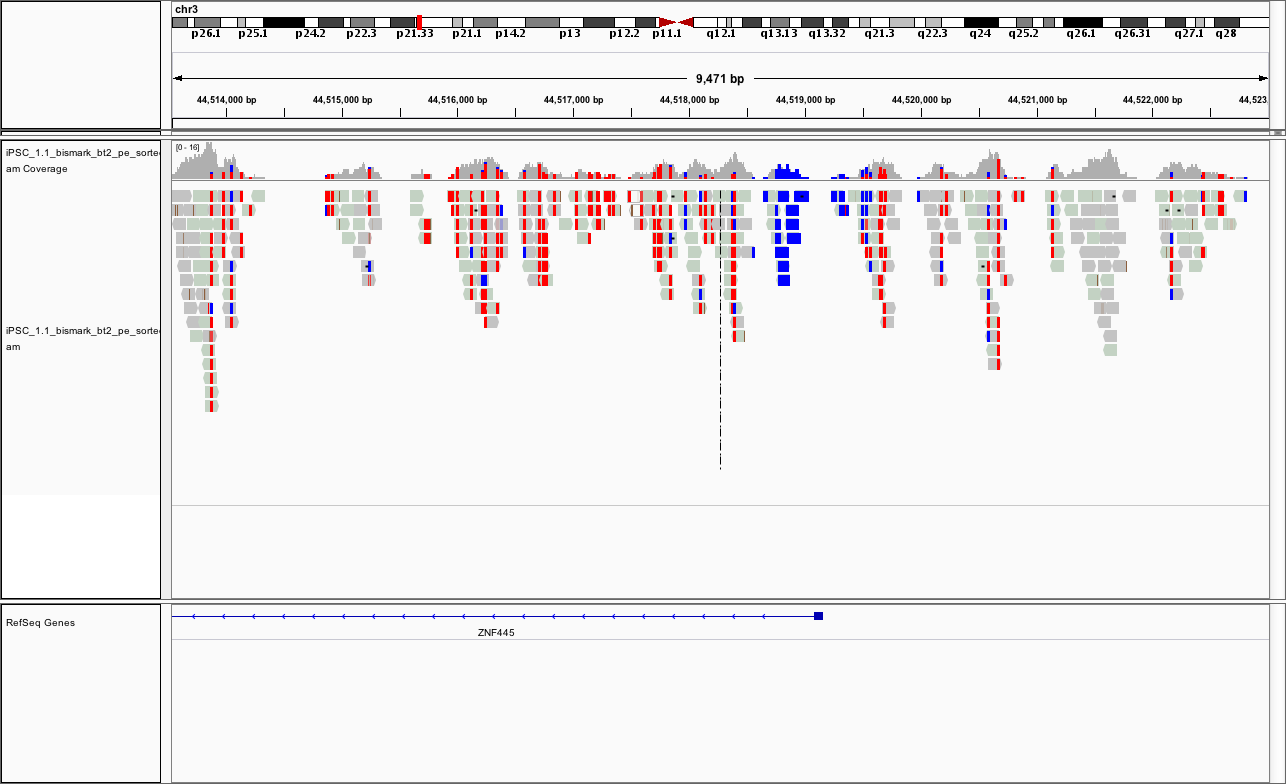
Repeat for the other replicate
Map using bismark
echo 'module load mugqic/bismark/0.16.1 ; module load mugqic/bowtie2/2.2.4 ; module load mugqic/samtools/1.3 ; \
bismark --bowtie2 -n 1 /gs/project/mugqic/bioinformatics.ca/epigenomics/wgb-seq/genome/ \
-1 data/iPSC_2.1.fastq -2 data/iPSC_2.2.fastq' | qsub -l nodes=1:ppn=4 -d .
Prepare files for IGV
echo 'module load mugqic/samtools/1.3 ; \
samtools sort iPSC_2.1_bismark_bt2_pe.bam -o iPSC_2.1_bismark_bt2_pe_sorted.bam ; \
samtools index iPSC_2.1_bismark_bt2_pe_sorted.bam' \
| qsub -l nodes=1:ppn=1 -d .
Check files
At this point you should have something like
[class99@lg-1r17-n02 module3]$ ls -ltr
total 59872
drwxr-xr-x 2 class99 class 512 Jun 20 16:56 data
-rw------- 1 class99 class 5107 Jun 20 17:21 STDIN.e60392695
-rw-r--r-- 1 class99 class 13964455 Jun 20 17:21 iPSC_1.1_bismark_bt2_pe.bam
-rw-r--r-- 1 class99 class 1862 Jun 20 17:21 iPSC_1.1_bismark_bt2_PE_report.txt
-rw------- 1 class99 class 4405 Jun 20 17:21 STDIN.o60392695
-rw------- 1 class99 class 61 Jun 20 17:25 STDIN.e60393634
-rw-r--r-- 1 class99 class 11653618 Jun 20 17:25 iPSC_1.1_bismark_bt2_pe_sorted.bam
-rw------- 1 class99 class 846 Jun 20 17:25 STDIN.o60393634
-rw-r--r-- 1 class99 class 1967480 Jun 20 17:25 iPSC_1.1_bismark_bt2_pe_sorted.bam.bai
-rw------- 1 class99 class 4404 Jun 20 17:36 STDIN.o60394706
-rw------- 1 class99 class 5111 Jun 20 17:36 STDIN.e60394706
-rw-r--r-- 1 class99 class 17226651 Jun 20 17:36 iPSC_2.1_bismark_bt2_pe.bam
-rw-r--r-- 1 class99 class 1862 Jun 20 17:36 iPSC_2.1_bismark_bt2_PE_report.txt
-rw------- 1 class99 class 61 Jun 20 17:51 STDIN.e60397285
-rw------- 1 class99 class 846 Jun 20 17:51 STDIN.o60397285
-rw-r--r-- 1 class99 class 14046478 Jun 20 17:51 iPSC_2.1_bismark_bt2_pe_sorted.bam
-rw-r--r-- 1 class99 class 2064608 Jun 20 17:51 iPSC_2.1_bismark_bt2_pe_sorted.bam.bai
Generate methylation profiles from the bam files
So far we have only mapped the reads using bismark. We can now generate methylation profiles using the following command
echo 'module load mugqic/bismark/0.16.1 ; module load mugqic/samtools/1.3 ; \
bismark_methylation_extractor --bedGraph iPSC_1.1_bismark_bt2_pe.bam' \
| qsub -l nodes=1:ppn=1 -d .
Do the same for the other replicate
echo 'module load mugqic/bismark/0.16.1 ; module load mugqic/samtools/1.3 ; \
bismark_methylation_extractor --bedGraph iPSC_2.1_bismark_bt2_pe.bam' \
| qsub -l nodes=1:ppn=1 -d .
Check files
At this point you should have something like
[class99@lg-1r17-n02 module3]$ ls
CHG_OB_iPSC_1.1_bismark_bt2_pe.txt CpG_OT_iPSC_2.1_bismark_bt2_pe.txt iPSC_2.1_bismark_bt2_pe.bedGraph.gz STDIN.e60397907
CHG_OB_iPSC_2.1_bismark_bt2_pe.txt data iPSC_2.1_bismark_bt2_pe.bismark.cov.gz STDIN.e60397937
CHG_OT_iPSC_1.1_bismark_bt2_pe.txt iPSC_1.1_bismark_bt2_pe.bam iPSC_2.1_bismark_bt2_pe.M-bias.txt STDIN.e60398115
CHG_OT_iPSC_2.1_bismark_bt2_pe.txt iPSC_1.1_bismark_bt2_pe.bedGraph.gz iPSC_2.1_bismark_bt2_PE_report.txt STDIN.o60392695
CHH_OB_iPSC_1.1_bismark_bt2_pe.txt iPSC_1.1_bismark_bt2_pe.bismark.cov.gz iPSC_2.1_bismark_bt2_pe_sorted.bam STDIN.o60393634
CHH_OB_iPSC_2.1_bismark_bt2_pe.txt iPSC_1.1_bismark_bt2_pe.M-bias.txt iPSC_2.1_bismark_bt2_pe_sorted.bam.bai STDIN.o60394706
CHH_OT_iPSC_1.1_bismark_bt2_pe.txt iPSC_1.1_bismark_bt2_PE_report.txt iPSC_2.1_bismark_bt2_pe_splitting_report.txt STDIN.o60397285
CHH_OT_iPSC_2.1_bismark_bt2_pe.txt iPSC_1.1_bismark_bt2_pe_sorted.bam STDIN.e60392695 STDIN.o60397907
CpG_OB_iPSC_1.1_bismark_bt2_pe.txt iPSC_1.1_bismark_bt2_pe_sorted.bam.bai STDIN.e60393634 STDIN.o60397937
CpG_OB_iPSC_2.1_bismark_bt2_pe.txt iPSC_1.1_bismark_bt2_pe_splitting_report.txt STDIN.e60394706 STDIN.o60398115
CpG_OT_iPSC_1.1_bismark_bt2_pe.txt iPSC_2.1_bismark_bt2_pe.bam STDIN.e60397285
Uncompress the bedGraph files
gunzip iPSC_1.1_bismark_bt2_pe.bedGraph.gz
gunzip iPSC_2.1_bismark_bt2_pe.bedGraph.gz
Transfer the files to your local computer
Using a different terminal window that is not connected to the server (if you are using Mac/Linux) or WinSCP (if you are using Windows), retrieve the iPSC_2.1_bismark_bt2_pe_sorted.bam and iPSC_2.1_bismark_bt2_pe_sorted.bam.bai
scp class%%@guillimin.clumeq.ca:/home/class%%/module3/iPSC_2.1_bismark_bt2_pe_sorted.bam* .
Also transfer the bedGraphs
scp class%%@guillimin.clumeq.ca:/home/class%%/module3/*bedGraph* .
Where you need to replace the two places with “%%” by your student number.
Load all the data in IGV
Load iPSC_1.1_bismark_bt2_pe.bedGraph in IGV using File -> Load from file.
Load iPSC_2.1_bismark_bt2_pe_sorted.bam in IGV using File -> Load from file.
Load iPSC_2.1_bismark_bt2_pe.bedGraph in IGV using File -> Load from file.
At this point, if you load the region chr3:44,513,532-44,523,018 you should see something like
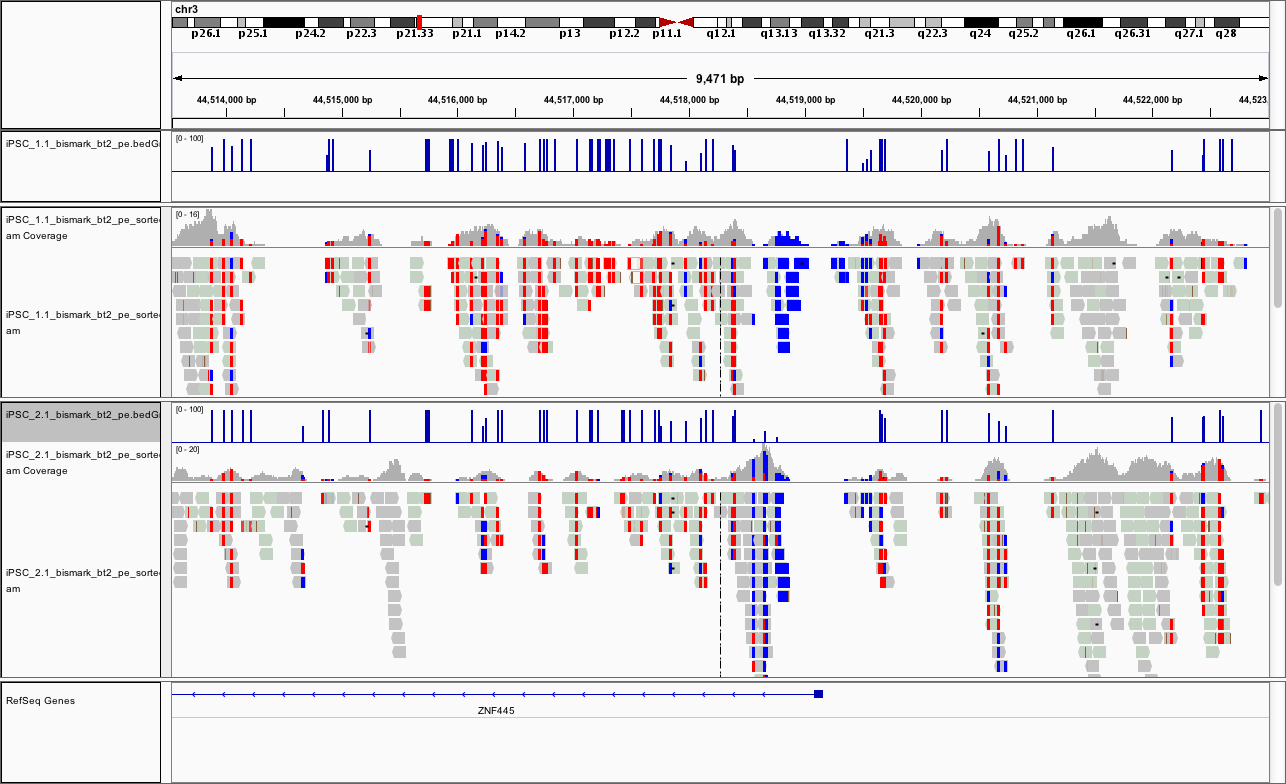
This promoter looks to be hypomethylated.
Can you find a promoter that is hypermethylated?
How about chr3:44,274,770-44,293,744?
Do you how to load CpG islands annotation?
Congrats, you’re done!
Continue exploring on your own…